Gene:CAV2
Gene:CFL2
Gene:FXYD1
Gene:GNG11
Gene:GSN
Gene:LEP
Gene:MGLL
Gene:MYLK
Gene:SEMA3G
Gene:SORBS1
Gene:PDE2A
Gene:ERBB2
Gene:ESR1
| Gene | CPG site | Chr | Location | Resign | Relationship |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAV2 | cg12739419 cg16260298 cg25274503 |
chr7 chr7 chr7 |
116500539 116500288 116500074 |
promoter, 1st intron, S_shore promoter, 1st intron, CGI Promoter, 1st intron, CGI |
hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) |
| CFL2 | cg25027125 | chr14 | 34713595 | 3rd intron, N_shore | hyper(-) |
| FXYD1 | cg03078169 cg05247914 cg07780528 cg17540545 cg18503912 cg22783327 |
chr19 chr19 chr19 chr19 chr19 chr19 |
35138887 35138797 35139430 35139451 35139375 35142354 |
promoter, N_shelf, N_shore promoter, N_shelf promoter, N_shelf promoter, N_shelf, N_shore promoter, N_shelf, N_shore 5th intron, N_shore |
hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) Hypo(-) |
| GNG11 | cg08038054 | chr7 | 93921469 | promoter | hyper(-) |
| GSN | cg13569051 cg13828579 cg14399183 |
chr9 chr9 chr9 |
121289425 121306136 121286030 |
5′UTR, 10th intron 12th intron 5′UTR, 10th intron |
hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) |
| LEP | cg00840332 cg07464571 cg12782180 cg13381984 cg19594666 cg26814075 |
chr7 chr7 chr7 chr7 chr7 chr7 |
128241216 128240948 128240879 128241291 128241227 128241245 |
promoter, CGI promoter, CGI promoter, CGI promoter, 5′UTR, 1st exon, CGI Promoter, CGI Promoter, CGI |
hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) |
| MGLL | cg18274619 | chr3 | 127776009 | enhancer, 4th intron | hyper(-) |
| MYLK | cg00465319 cg18731398 |
chr3 chr3 |
123620721 123695886 |
3rd intron 16th intron |
hyper(-) hyper(-) |
| SEMA3G | cg11137980 | chr3 | 52435210 | 5′UTR, 1st exon | hyper(-) |
| SORBS1 | cg02370232 cg06282596 |
chr10 chr10 |
95415608 95415722 |
18th intron 18th intron |
hyper(-) hyper(-) |
| PDE2A | cg16640865 | chr11 | 72590514 | 24th exon, CGI | Hypo(-) |
| ERBB2 | cg24657085 cg00459816 |
37860344 37862113 |
enhancer enhancer |
Hypo(+) Hypo(+) |
|
| ESR1 | cg22157087 cg17741339 cg18132851 cg23009221 cg07455133 |
152012887 152085619 152085641 152128588 152379044 |
enhancer enhancer enhancer enhancer enhancer |
Hypo(+) Hypo(+) Hypo(+) Hypo(+) Hypo(+) |
Gene:CEBPA
Gene:FBLN2
Gene:FAT4
| Gene | CPG site | Chr | Location | Resign | Relationship |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEBPA | cg01437571 cg10099799 cg06621373 cg02493939 |
33792148 33794556 33794690 33794746 |
Island Island Island Island |
hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) |
|
| FBLN2 | cg19392656 cg16604516 cg17561417 cg18603228 cg01896761 cg18406197 cg12700904 cg00201234 |
13590415 13590419 13590432 13590439 13590444 13590450 13590720 13590968 |
Island Island Island Island Island Island Island Island |
hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) |
|
| FAT4 | cg12828819 cg04459504 cg05118638 cg10731073 cg08644023 cg03527919 cg15795630 cg03404279 cg22911422 cg12058185 cg23901852 cg17265829 cg08575049 cg04373334 |
12623686 12623735 12623731 12623733 12623741 12623744 12623753 12623757 12623796 12623827 12623834 12623842 12623888 12623899 |
Island Island Island Island Island Island Island Island Island Island Island Island Island Island |
hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) |
| Gene | CPG site | Chr | Location | Resign | Relationship |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAV2 | cg12739419 cg16260298 cg25274503 |
chr7 chr7 chr7 |
116500539 116500288 116500074 |
promoter, 1st intron, S_shore promoter, 1st intron, CGI Promoter, 1st intron, CGI |
hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) |
| CFL2 | cg25027125 | chr14 | 34713595 | 3rd intron, N_shore | hyper(-) |
| GSN | cg13569051 cg13828579 cg14399183 |
chr9 chr9 chr9 |
121289425 121306136 121286030 |
5′UTR, 10th intron 12th intron 5′UTR, 10th intron |
hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) |
| LEP | cg00840332 cg07464571 cg12782180 cg13381984 cg19594666 cg26814075 |
chr7 chr7 chr7 chr7 chr7 chr7 |
128241216 128240948 128240879 128241291 128241227 128241245 |
promoter, CGI promoter, CGI promoter, CGI promoter, 5′UTR, 1st exon, CGI Promoter, CGI Promoter, CGI |
hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) |
| MYLK | cg00465319 cg18731398 |
chr3 chr3 |
123620721 123695886 |
3rd intron 16th intron |
hyper(-) hyper(-) |
| SORBS1 | cg02370232 cg06282596 |
chr10 chr10 |
95415608 95415722 |
18th intron 18th intron |
hyper(-) hyper(-) |
| ERBB2 | cg24657085 cg00459816 |
37860344 37862113 |
enhancer enhancer |
Hypo(+) Hypo(+) |
|
| ESR1 | cg22157087 cg17741339 cg18132851 cg23009221 cg07455133 |
152012887 152085619 152085641 152128588 152379044 |
enhancer enhancer enhancer enhancer enhancer |
Hypo(+) Hypo(+) Hypo(+) Hypo(+) Hypo(+) |
| Gene | CPG site | Chr | Location | Resign | Relationship |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEBPA | cg01437571 cg10099799 cg06621373 cg02493939 |
33792148 33794556 33794690 33794746 |
Island Island Island Island |
hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) |
|
| FBLN2 | cg19392656 cg16604516 cg17561417 cg18603228 cg01896761 cg18406197 cg12700904 cg00201234 |
13590415 13590419 13590432 13590439 13590444 13590450 13590720 13590968 |
Island Island Island Island Island Island Island Island |
hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) |
|
| FAT4 | cg12828819 cg04459504 cg05118638 cg10731073 cg08644023 cg03527919 cg15795630 cg03404279 cg22911422 cg12058185 cg23901852 cg17265829 cg08575049 cg04373334 |
12623686 12623735 12623731 12623733 12623741 12623744 12623753 12623757 12623796 12623827 12623834 12623842 12623888 12623899 |
Island Island Island Island Island Island Island Island Island Island Island Island Island Island |
hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) |
| Gene | CPG site | Chr | Location | Resign | Relationship |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FXYD1 | cg03078169 cg05247914 cg07780528 cg17540545 cg18503912 cg22783327 |
chr19 chr19 chr19 chr19 chr19 chr19 |
35138887 35138797 35139430 35139451 35139375 35142354 |
promoter, N_shelf, N_shore promoter, N_shelf promoter, N_shelf promoter, N_shelf, N_shore promoter, N_shelf, N_shore 5th intron, N_shore |
hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) hyper(-) Hypo(-) |
| GNG11 | cg08038054 | chr7 | 93921469 | promoter | hyper(-) |
| MGLL | cg18274619 | chr3 | 127776009 | enhancer, 4th intron | hyper(-) |
| SEMA3G | cg11137980 | chr3 | 52435210 | 5′UTR, 1st exon | hyper(-) |
| PDE2A | cg16640865 | chr11 | 72590514 | 24th exon, CGI | Hypo(-) |
By analyzing breast cancer, paracancerous tissue, breast tumor and normal samples, the following conclusions were obtained:
- ➤ Hypomethylation of the gene body region was associated with upregulation of gene expression and contributed to enhanced or activated gene expression in cancer tissues. Hypermethylation of the TSS1500, 5'UTR , and first exon regions was associated with gene down-regulation and resulted in diminished gene expression in breast cancer tissues.
- ➤ The 3'UTR is overall biased towards hypermethylation. Enhancers tend to be hypermethylated,and enhancer hypermethylation is associated with upregulation of breast cancer gene expression and increased expression of breast carcinogenesis oncogenes.
- ➤ CGI is predominantly hyper-methylated, while shores and shelves are more likely to be hypomethylated. Hypermethylation differences in the CGI region are associated with downregulation of gene expression, and hypomethylation in the shores region is associated with upregulation of gene expression. The DNA methylation distribution in both shores regions was scattered, while the DNA methylation distribution in CpG islands was more concentrated.CGI hypermethylation of promoters suppresses gene expression.
- ➤ The cg14399183 and cg13569051 probes located in intron 10 of the GSN gene are protective factors against breast cancer, while the cg25274503 probe located in the first intron of the CAV2 gene is a risk factor for breast cancer.
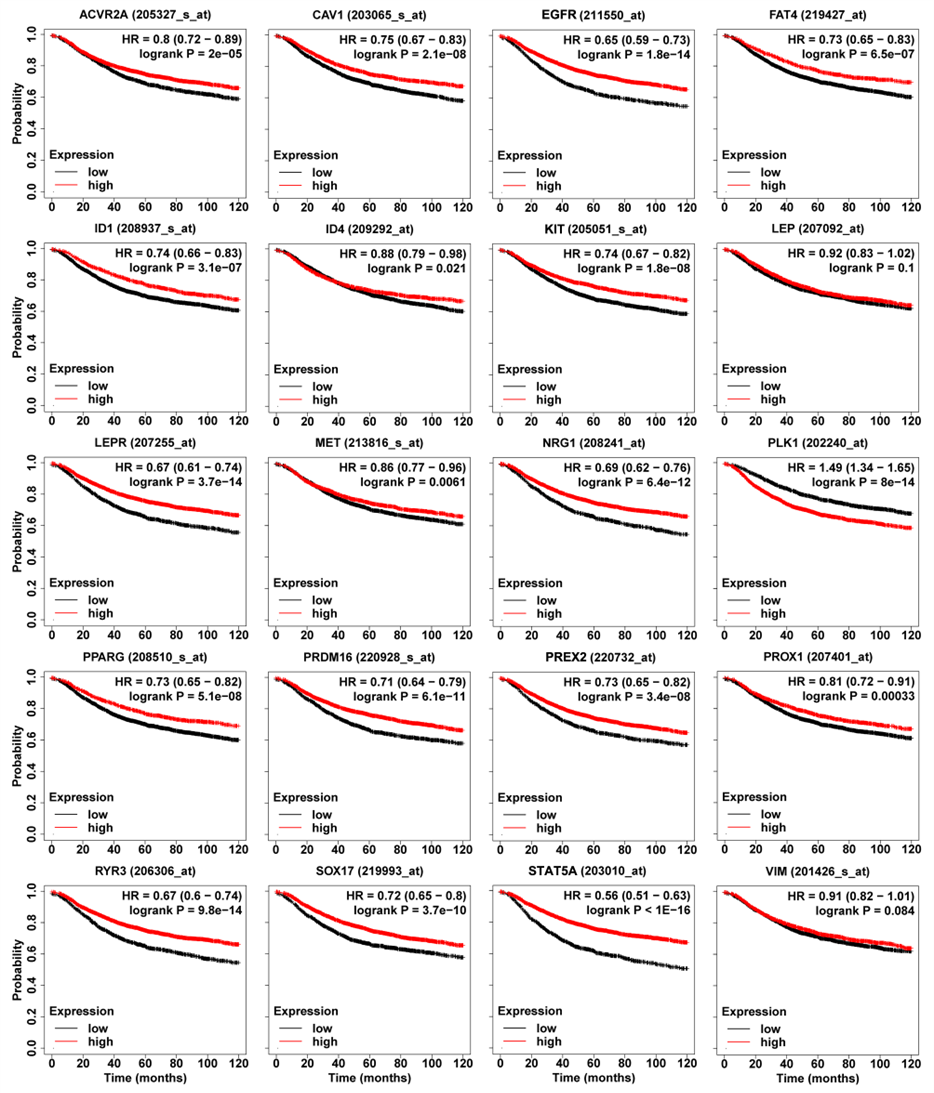
- ➤ PLK1 was an oncogene. In contrast, the high expression of the 17 genes (EGFR (211550_at), ACVR2A (205327_s_at), C AV 1 (203065_s_at), FAT4 (219427_at), ID1 (208937_s_at), ID4 (209292_at), KIT (205051_s_at), LEPR (207255_ at), MET (213816_s_at), NRG1 (208241_at), PPARG (208510_s_at), PRDM16 (220928_s_at), PREX2 (220732_at), PROX1 (207401_at), RYR3 (206306_at), SOX17 (219993_at), and STAT5A (203010_at)) could significantly improve the prognosis of breast cancer patients. However, the high expression of LEP (207092_ at) and VIM (201426_s_at) were weakly correlated with a good prognosis.
Gene:CAV2
Gene:GSN
| Gene | CPG site | Chr | Location | Resign | Relationship |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAV2 | cg25274503 | chr7 | 116500074 | promoter, 1st intron, CGI | hyper(-) |
| GSN | cg13569051 cg14399183 |
chr9 chr9 |
121289425 121286030 |
5′UTR, 10th intron 5′UTR, 10th intron |
hyper(-) hyper(-) |
Morbi tincidunt, dui sit amet facilisis feugiat, odio metus gravida ante, ut pharetra massa metus id nunc. Duis scelerisque molestie turpis. Sed fringilla, massa eget luctus malesuada, metus eros molestie lectus, ut tempus eros massa ut dolor.
Gene:TPD52
| Gene | HM | Distribution | Location | Relationship | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPD52 | H3K36me3 |  |
(-400, 1400) | Promoter | Up(+) | |
| H3K79me2 |  |
(400, 1200) | Promoter | Up(+) | ||
| H3K27ac | 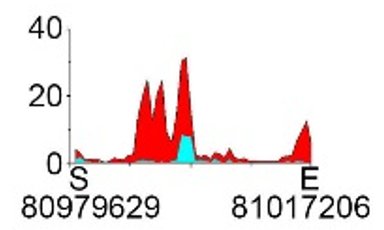 |
chr8 | super enhancer | Up(+) | ||
| H3K9ac | 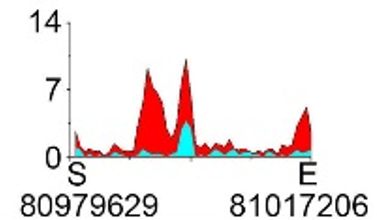 |
chr8 | super enhancer | Up(+) |
Gene:NRG1
Gene:GADD45A
| Gene | HM | Distribution | Location | Relationship | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRG1 | H3K36me3 | 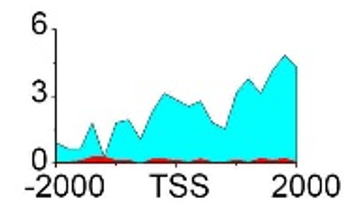 |
(-2000, 2000) | Promoter | Up(-) | |
| H3K79me2 | 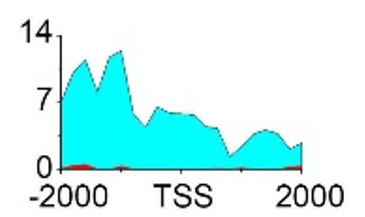 |
(-2000, 2000) | Promoter | Up(-) | ||
| H3K27ac | 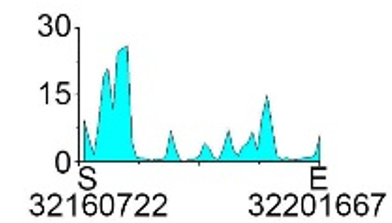 |
chr8 | super enhancer | Up(-) | ||
| H3K9ac | 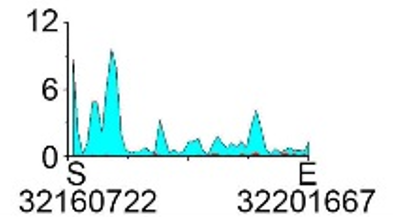 |
chr8 | super enhancer | Up(-) | ||
| GADD45A | H3K36me3 | 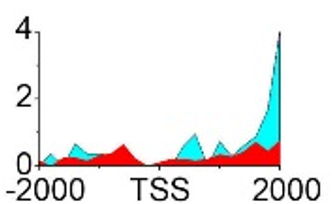 |
(1600, 2000) | Promoter | Up(-) | |
| H3K79me2 | 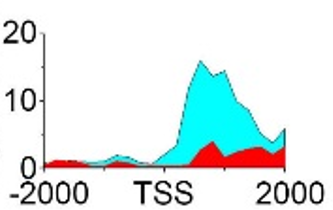 |
(TSS, 1200) | Promoter | Up(-) | ||
| H3K27ac |  |
chr1 | super enhancer | Up(-) | ||
| H3K9ac | 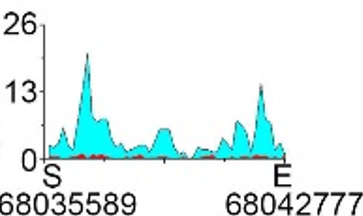 |
chr1 | super enhancer | Up(-) |
| Gene | HM | Distribution | Location | Relationship | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPD52 | H3K36me3 |  |
(-400, 1400) | Promoter | Up(+) | |
| H3K79me2 |  |
(400, 1200) | Promoter | Up(+) | ||
| H3K27ac |  |
chr8 | super enhancer | Up(+) | ||
| H3K9ac |  |
chr8 | super enhancer | Up(+) |
| Gene | HM | Distribution | Location | Relationship | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRG1 | H3K36me3 |  |
(-2000, 2000) | Promoter | Up(-) | |
| H3K79me2 |  |
(-2000, 2000) | Promoter | Up(-) | ||
| H3K27ac |  |
chr8 | super enhancer | Up(-) | ||
| H3K9ac |  |
chr8 | super enhancer | Up(-) | ||
| GADD45A | H3K36me3 |  |
(1600, 2000) | Promoter | Up(-) | |
| H3K79me2 |  |
(TSS, 1200) | Promoter | Up(-) | ||
| H3K27ac |  |
chr1 | super enhancer | Up(-) | ||
| H3K9ac |  |
chr1 | super enhancer | Up(-) |
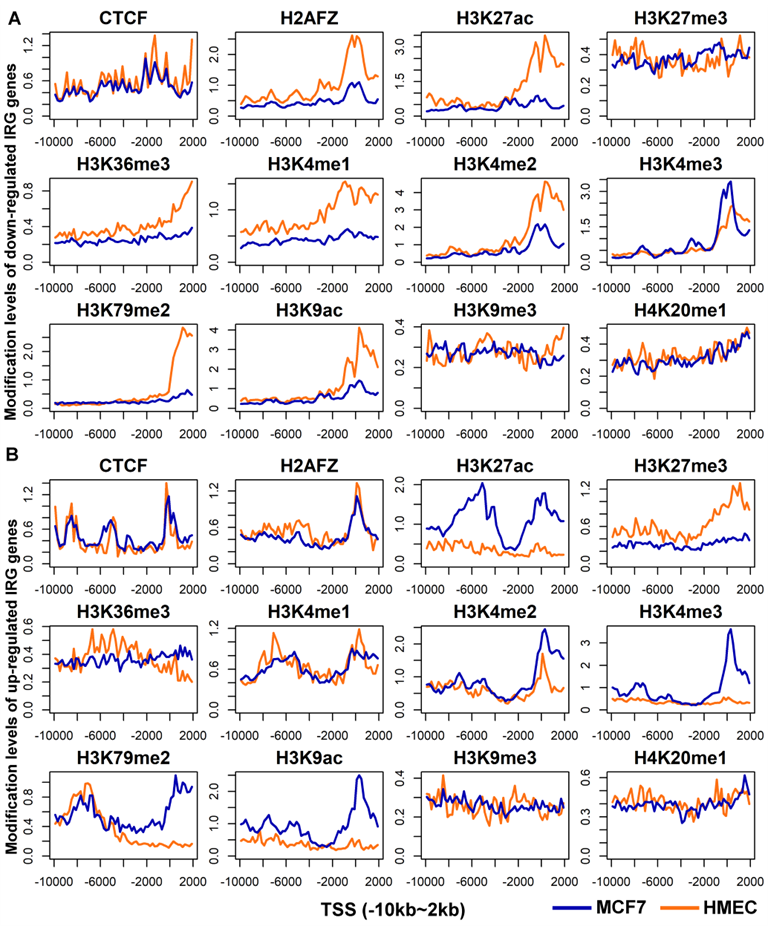
By analyzing histone modification levels of differentially expressed genes between human breast cancer cells (MCF-7) and human normal mammary epithelial cells (HMEC), the following conclusions were obtained:
- ➤ Elevated levels of H3K79me2 modification downstream of TSS lead to upregulated gene expression.
- ➤ Elevated levels of H3K27ac in TSS flanking modifications lead to down-regulated gene expression.
- ➤ GADD45A and NRG1 are protective factors for breast cancer, and TPD52 is a risk factor for breast cancer.
✦(B) The distribution map of the modification levels of 11 histone modifications and 1 transcription factor for up-regulated genes in MCF7 and HMEC cell

✦(B) The distribution map of the modification levels of 11 histone modifications and 1 transcription factor for up-regulated IRG genes in MCF7 and HMEC cell lines.
| Gene | HM | Distribution | Location | Relationship | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPD52 | H3K36me3 |  |
(-400, 1400) | Promoter | Up(+) | |
| H3K79me2 |  |
(400, 1200) | Promoter | Up(+) | ||
| H3K27ac |  |
chr8 | super enhancer | Up(+) | ||
| H3K9ac |  |
chr8 | super enhancer | Up(+) |
| Gene | HM | Distribution | Location | Relationship | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRG1 | H3K36me3 |  |
(-2000, 2000) | Promoter | Up(-) | |
| H3K79me2 |  |
(-2000, 2000) | Promoter | Up(-) | ||
| H3K27ac |  |
chr8 | super enhancer | Up(-) | ||
| H3K9ac |  |
chr8 | super enhancer | Up(-) | ||
| GADD45A | H3K36me3 |  |
(1600, 2000) | Promoter | Up(-) | |
| H3K79me2 |  |
(TSS, 1200) | Promoter | Up(-) | ||
| H3K27ac |  |
chr1 | super enhancer | Up(-) | ||
| H3K9ac |  |
chr1 | super enhancer | Up(-) |
Lncrnas that act synergistically with methylation on target genes:
| SRHC | HULC | PCAT-14 | HOTAIR | BZRAP1-AS1 | FENDRR | HOXA11-AS |
|---|
Conclusion
Long noncoding RNA SRHC is highly expressed in normal liver tissue, but its expression in HCC is significantly reduced or lacking.Overexpression of this long noncoding RNA can inhibit cancer cell proliferation.Cloning experiments confirmed that, after overexpression of the gene,the clone-forming ability of cancer cells significantly decreases.The promoter region of SRHC contains a CpG-rich island and that SRHC is down-regulated in tumors at least partly by DNA methylation.
Regulatory Mechanism
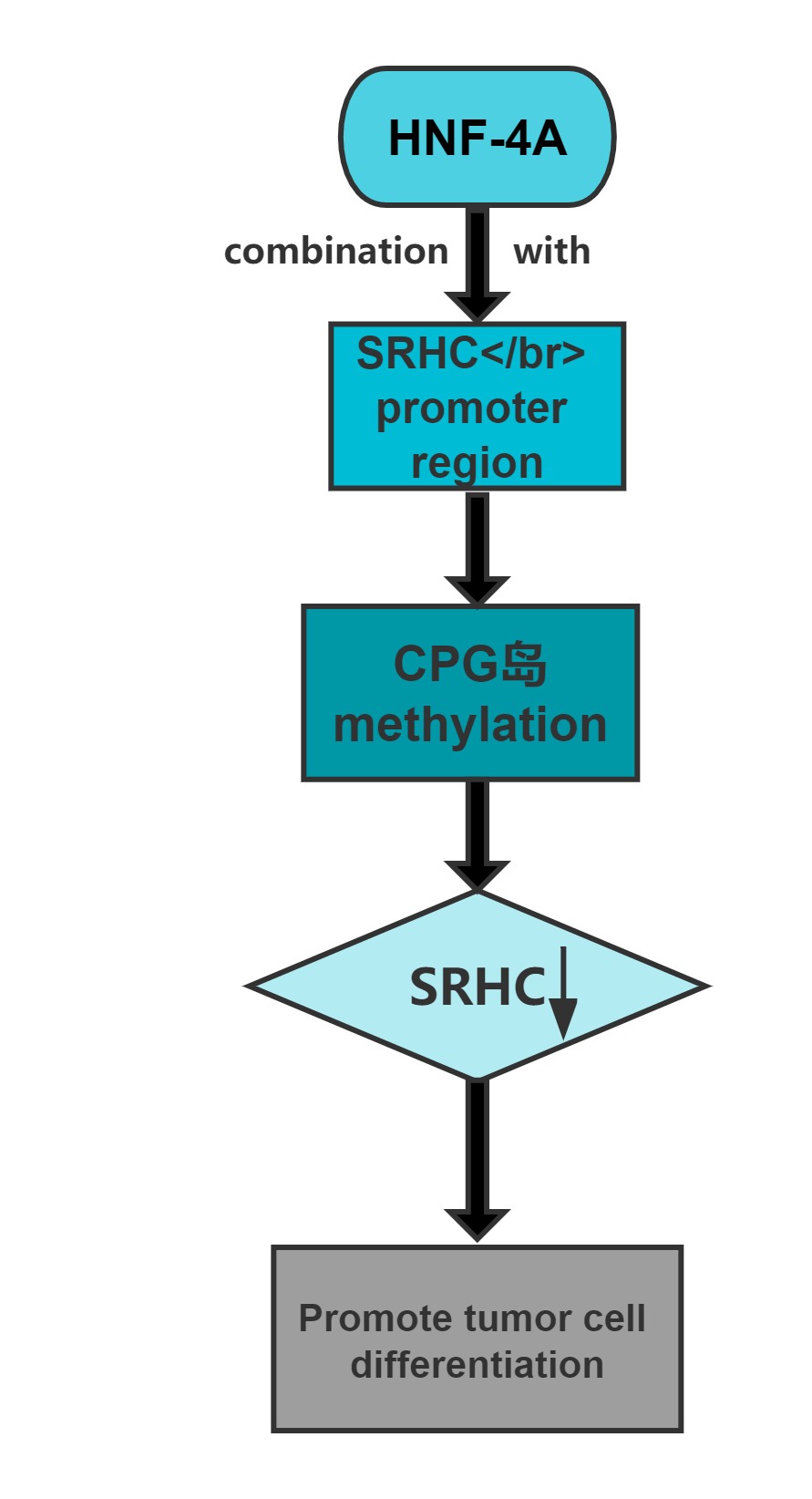
Conclusion
HULC elicits the methylation of CpG islands in the miR-9 promoter, resulting in the suppression of miR-9 expression. MiR-9 is able to target the 3’UTR of transcription factor PPARA, and the decrease in miR-9 leads to upregulation of PPARA and the subsequent transactivation of ACSL1, which enhances lipogenesis and enriches intracellular triglycerides and cholesterol in hepatoma cells. Thus, HULC-enhanced abnormal lipid metabolism accelerates the growth of liver cancer.Furthermore, the cholesterol product of ACSL1 upregulates HULC by activating the transcription factor RXRA, forming a positive feedback loop with HULC/miR-9/PPARA/ACSL1/cholesterol/RXRA/HULC in hepatoma cells.
Regulatory Mechanism
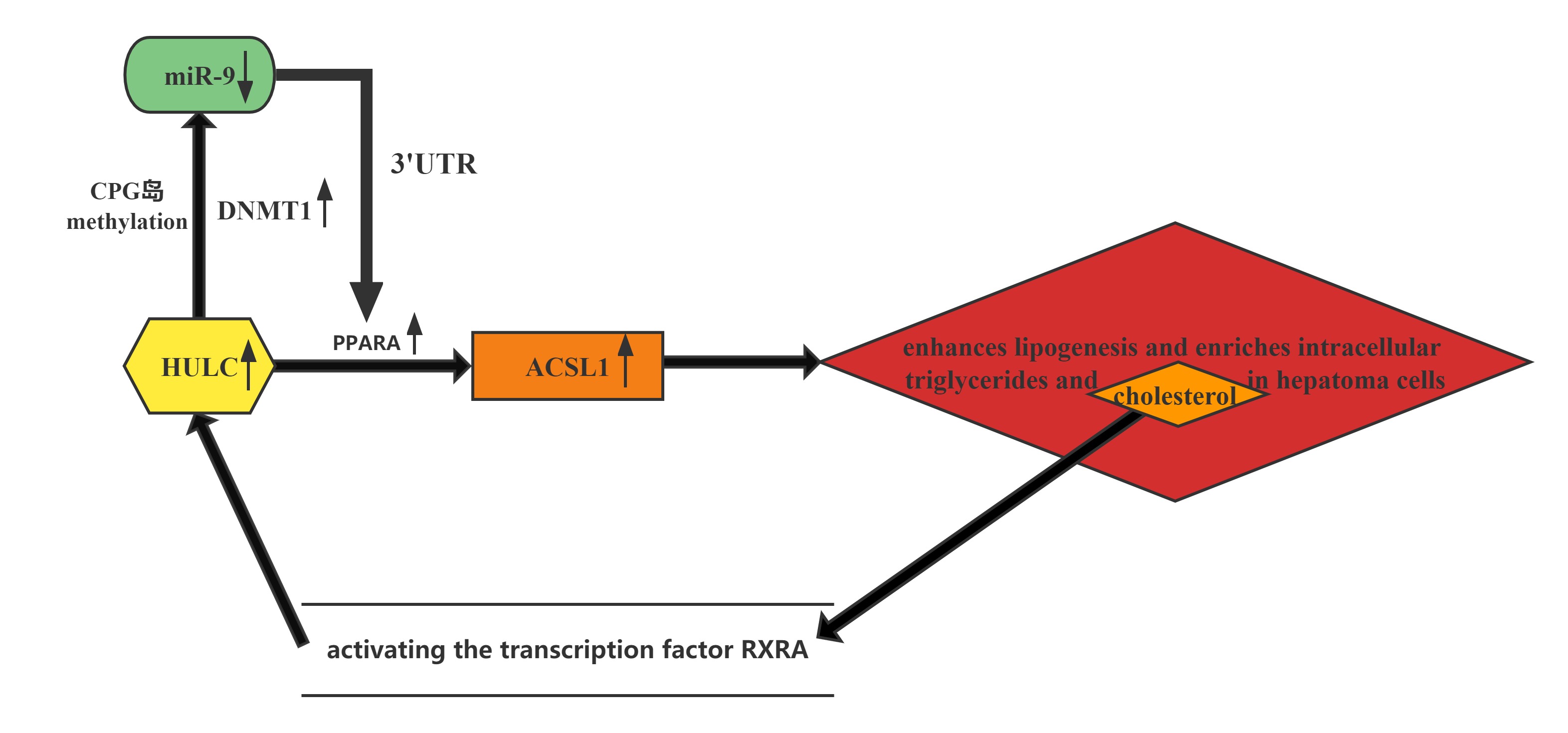
Conclusion
HCC tissues and cells express high levels of PCAT-14, PCAT-14 inhibits miR-372 expression by inducing the methylation of CpG islands in the miR-372 promoter. ATAD2 is one of the target genes of miR-372, and regulates the Hh pathway to influence HCC proliferation and metastasis. PCA T-14 regulates A TAD2 expression and Hedgehog pathway via miR-372. Together, these findings indicate that PCA T-14 plays an important role in HCC carcinogenesis and may provide a new target for HCC detection and treatment.
Regulatory Mechanism
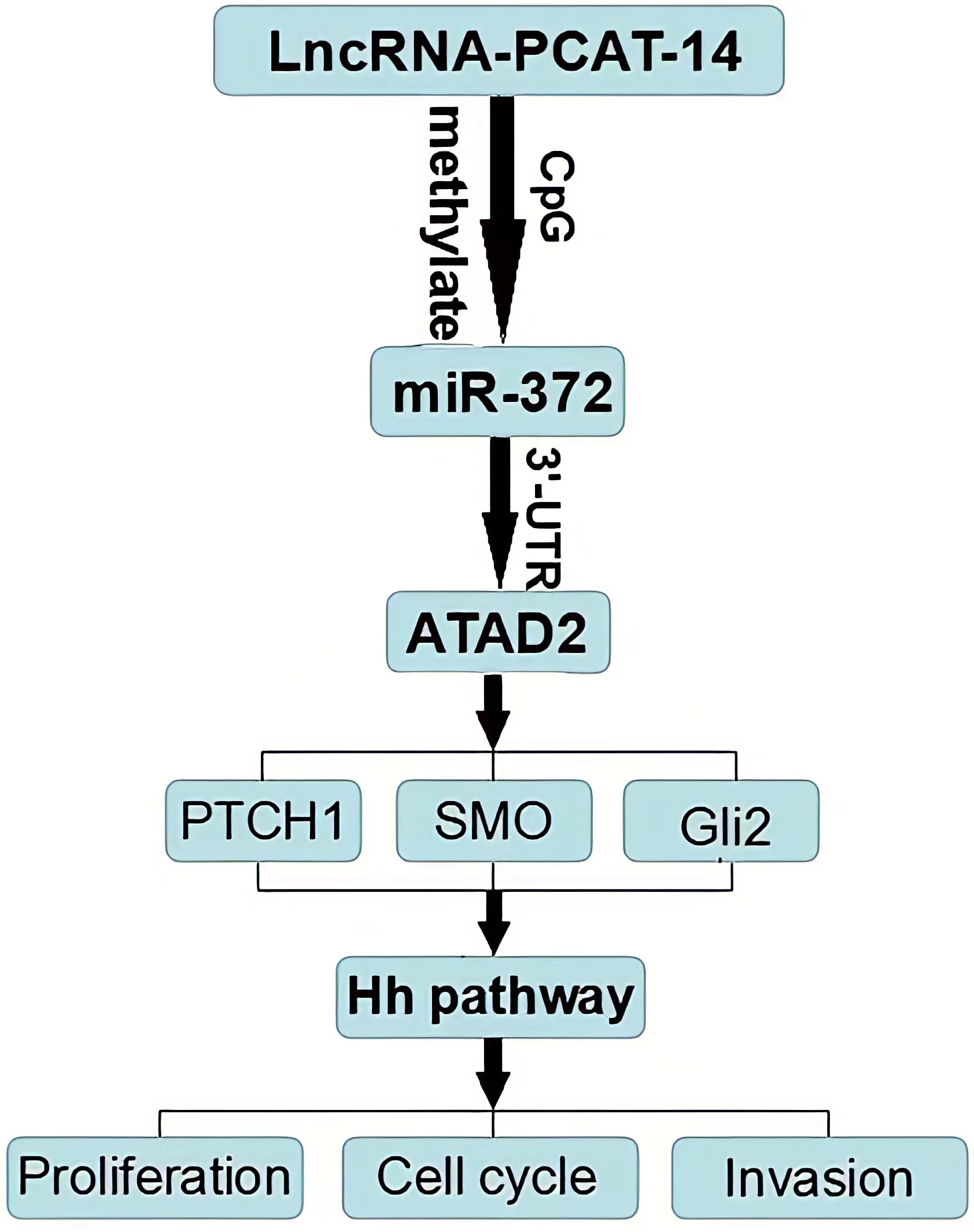
Conclusion
HOTAIR in HCC cells decreased DNA methylation level of miR-122 promoter region, resulting in elevated expression of miR-122.HOTAIR could upregulate DNMTs expression via EZH2, contributing to modulation of DNA methylationat the miR-122 promoter region and consequently suppression of miR-122 expression.As a well-known tumor suppressor against HCC, miR-122 has been reported to inhibit cell growth and suppress tumorigenesis by negatively regulating its targetsCyclin G1, a key cell cycle protein, plays an essential role in tumor growth, has been shown to be a target of miR-122, and highly expressed in HCC cells.MiR-122 negatively regulated Cyclin G1 expression in HCC cells.HOTAIR upregulated Cyclin G1 expression via suppression of miR-122, implicating that HOTAIR would play an important role in cell cycle regulation through the miR-122/Cyclin G1 pathway.
Regulatory Mechanism
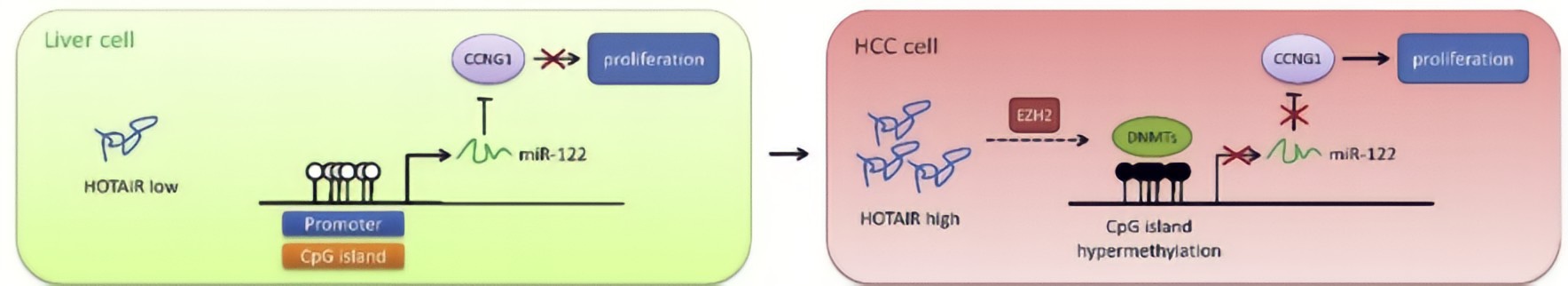
Conclusion
BZRAP1-AS1 was observed to recruit DNMT3b on the promoter region of THBS1, by which BZRAP1-AS1 can induce THBS1 DNA methylation, thereby repressing the transcription of THBS1.BZRAP1-AS1 silencing impedes tumor angiogenesis through increase of THBS1 BZRAP1-AS1 can be a potential therapeutic target to restrain tumor growth in HCC.
Regulatory Mechanism
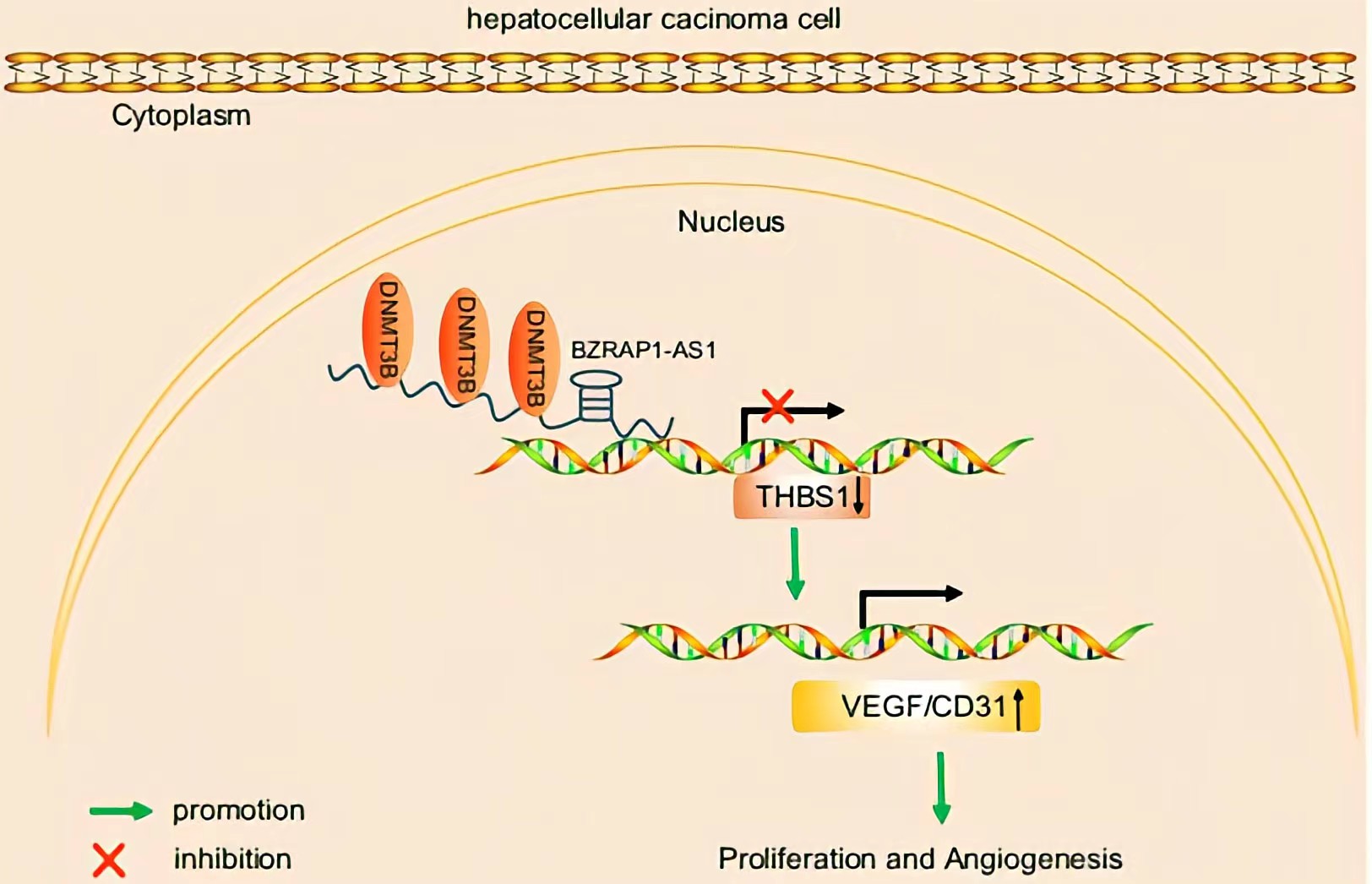
Conclusion
FENDRR bound to the promoter region of GPC3. The interaction of FENDRR with GPC3 promoter led to methylation of its promoter region. It has been known that methylation is sufficient to silence the GPC3 promoter, which resulted in transcriptional repression of GPC3 expression. FENDRR inhibited HCC growth and invasiveness, at least partially through targeting GPC3 at the epigenetic level. Restoration of FENDRR may be a potential approach to prevent HCC progression and metastasis.
Regulatory Mechanism
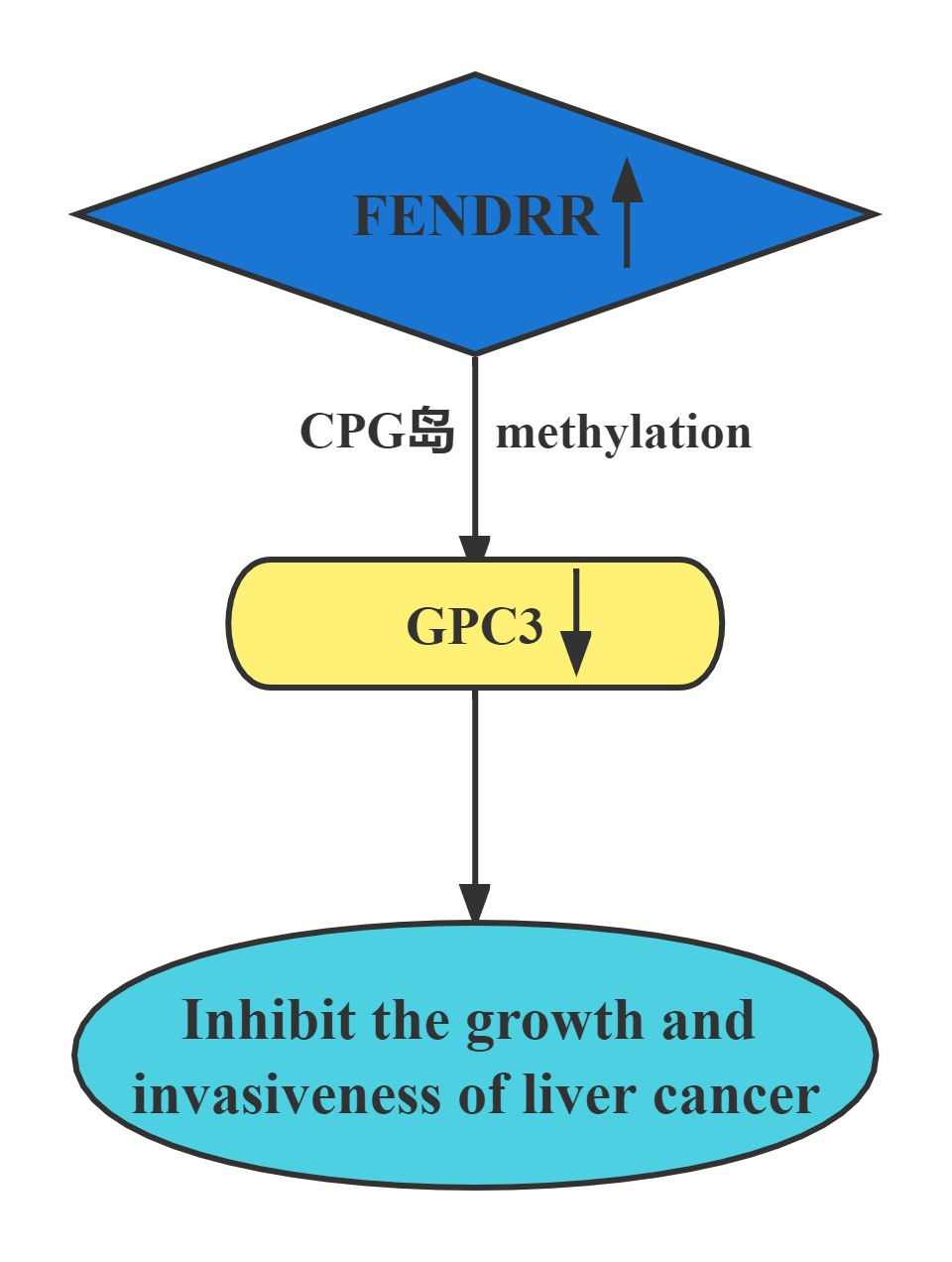
Conclusion
HOXA11-AS silencing promotes HOXA11 expression and inhibits the Wnt signaling pathway, subsequently reducing HCC stem cell proliferation, invasion, and self-renewal. These findings demonstrate a novel regulatory mechanism by which HOXA11-AS recruits DNMT1 to methylate the HOXA11 promoter, thus repressing HOXA11 transcription.
Regulatory Mechanism
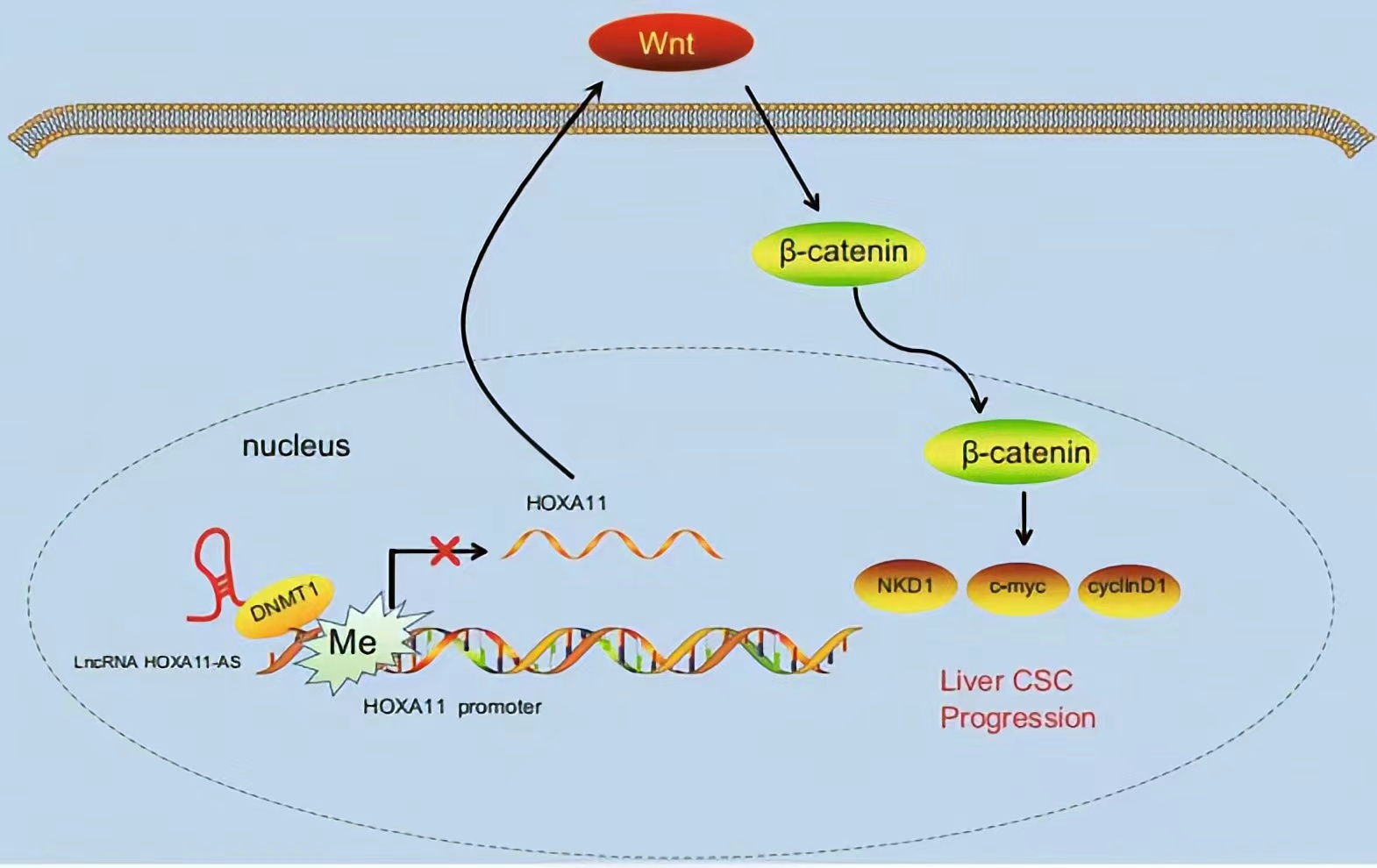
Lncrnas that act synergistically with histone modification on target genes:
Methylation: |
UCA1 | GAS8-AS1 | HOTAIR | TRERNA1 | DLX6-AS1 | LINC01419 |
|---|
Acetylation: |
GPC3 | Lnc-Myd88 |
|---|
Conclusion
UCA1 was one of the most upregulated lncRNAs by HBx.UCA1 repressed p27 expression via recruiting EZH2 and elevating its 3MeK27H3 level across the promoter via RIP and CHIP assays.UCA1, upregulated by HBx, displayed a crucial role in G1/S transition in both hepatic and hepatoma cells. More importantly, a positive correlation between the expression of UCA1 and HBx and a negative correlation between UCA1 and p27 were observed in HCC specimens, suggesting the significance of UCA1 in HBx-mediated hepatocarinogenesis.
Regulatory Mechanism
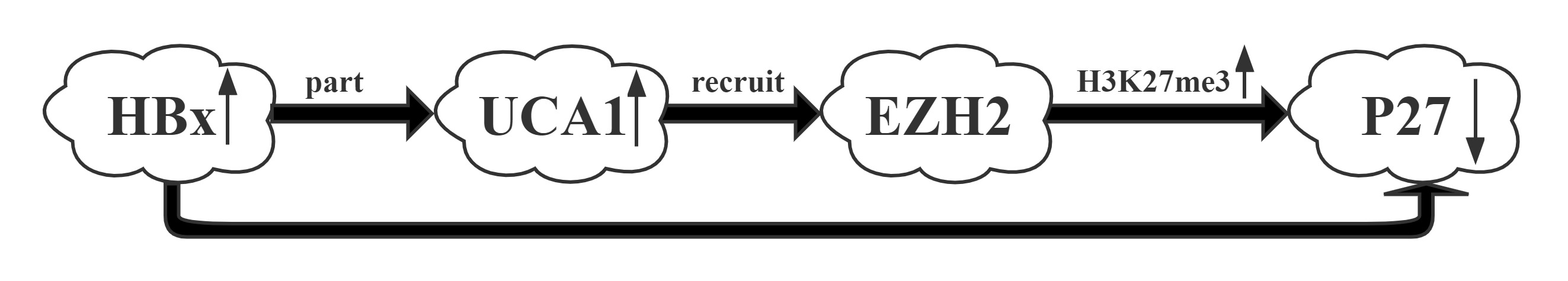
Conclusion
LncRNA HOTAIR which recruits the polycomb repressive complex 2 with its H3 lysine27 histone methylation activity, is overexpressed and decreases the expression of miR-122 in HCC tissues. As a well-known oncogene in most tumors, both in vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrated that knockdown of HOTAIR inhibited HCC cells proliferation, induced cell cycle arrest and suppressed tumor progression by negatively regulating miR-122 and consequently suppressing Cyclin G1.
Regulatory Mechanism
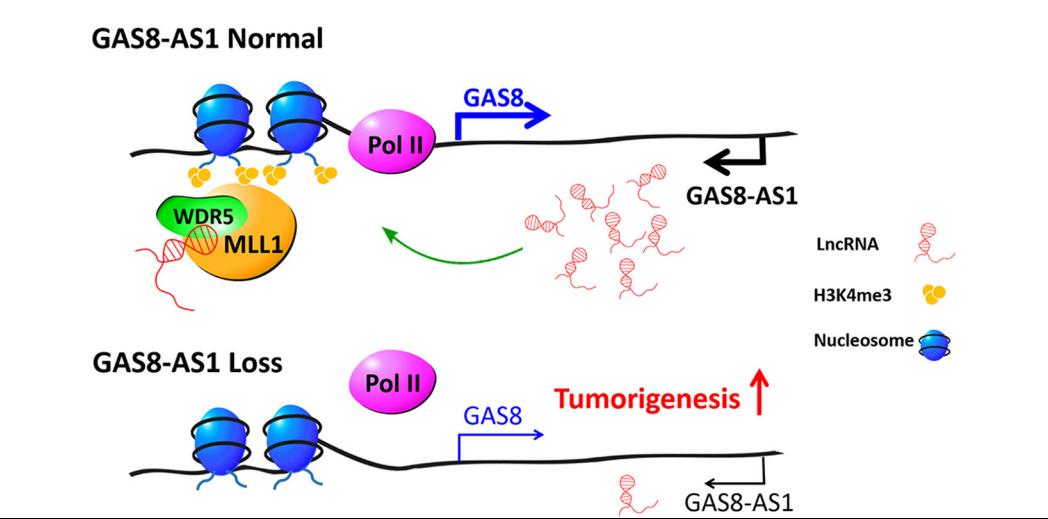
.jpg)
Conclusion
LncRNA GAS8-AS1 is required to maintain the GAS8 promoter in an open chromatin state. In accord with this notion, knockdown of GAS8-AS1 results in reduced MLL1/WDR5 binding, decreased H3K4me3 levels, diminished RNA Pol II functions, and gene silencing of GAS8. Thus, lncRNA GAS8-AS1 may function as part of a surveillance mechanism that maintains activation of GAS8 promoter and transcription, which thus prevents carcinogenesis.
Regulatory Mechanism
Conclusion
TRERNA1 recruited EHMT2 to dimethylate H3K9 in the CDH1 promoter region. Given that lncRNAs are involved in histone methylation modification, they have become important epigenetic regulatory molecules during the regulation of target genes. EHMT2, a major histone methyltransferase for H3K9 me2, is a crucial modifying factor that is regulated during gene silencing. SNAI1 acts as a repressor of CDH1 and binds to EHMT2, which indicates that EHMT2 decreases CDH1 expression not only by dimethylation but also by interacting with SNAI1. In a transwell assay, TRERNA1 enhanced the metastatic ability of SNAI1 in HCC cells.In summary , The elevated lncRNA TRERNA1 levels promoted HCC cell metastasis in vitro and in vivo, the aberrant expression of TRERNA1 relates to metastatic HCC and a poor prognosis for patients. TRERNA1 suppresses CDH1 with epigenetic histone modifications via the recruitment of EHMT2 and/ or the EHMT2/SNAI1 complex. Therefore, targeting the lncRNA TRERNA1 might be a novel therapeutic strategy for metastatic HCC.
Regulatory Mechanism
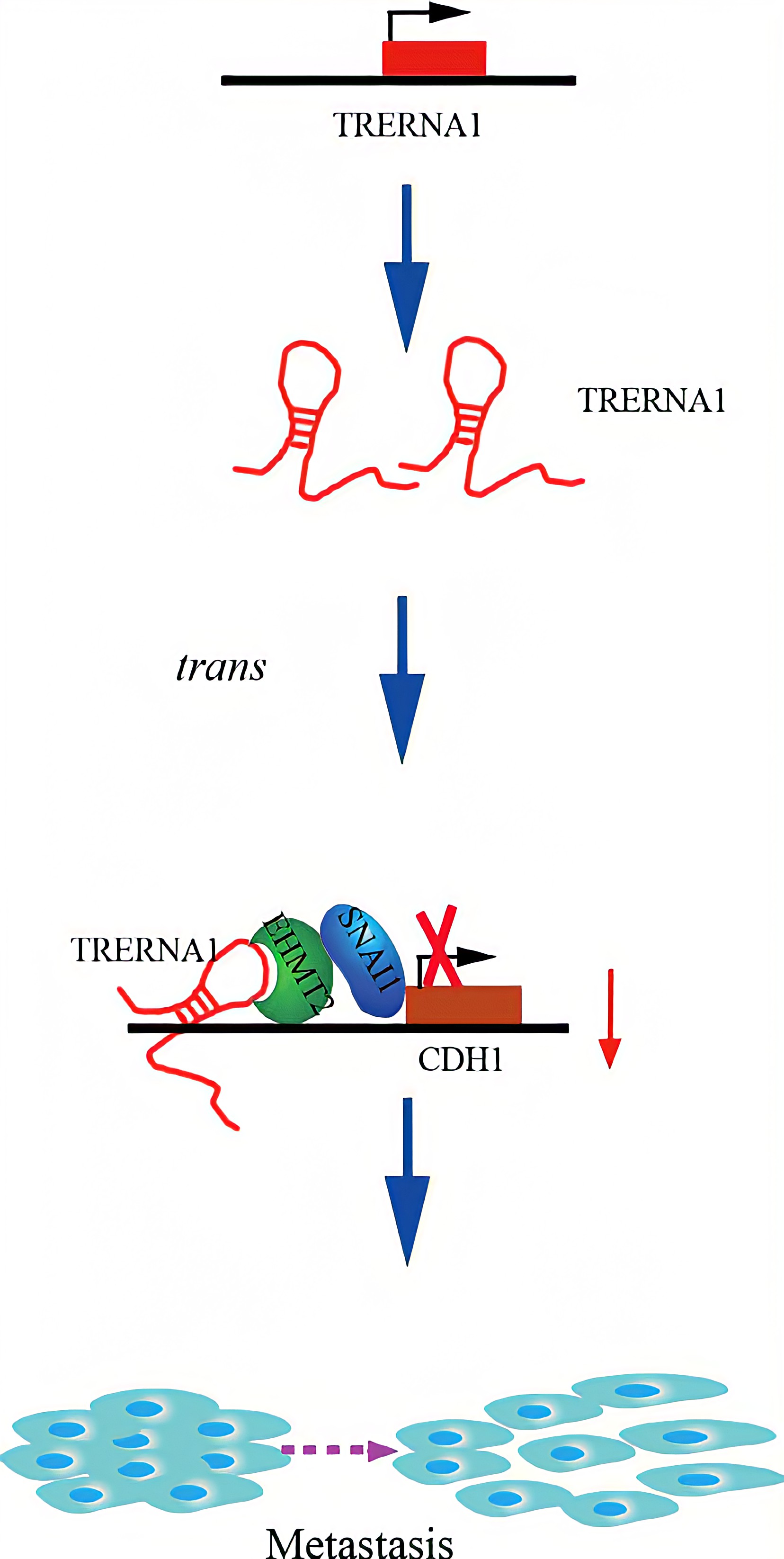
Conclusion
CADM1, a member belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily of cell adhesion molecule, is an extensively known tumor suppressor.LncRNA DLX6-AS1 was able to lead to a reduction in CADM1 expression by increasing CADM1 methylation, thus activating the STAT3 signaling pathway. STAT3 is a potent modulator of tumorigenesis, survival, and inflammation of liver cells, is constitutively activated in the vast majority of HCC cells.Silencing of lncRNA DLX6-AS1 enforced the expression of CADM1 and inactivated the STAT3 signaling pathway by suppressing CADM1 promoter methylation, thus repressing the tumorigenesis and tumor progression of LCSCs.
Regulatory Mechanism
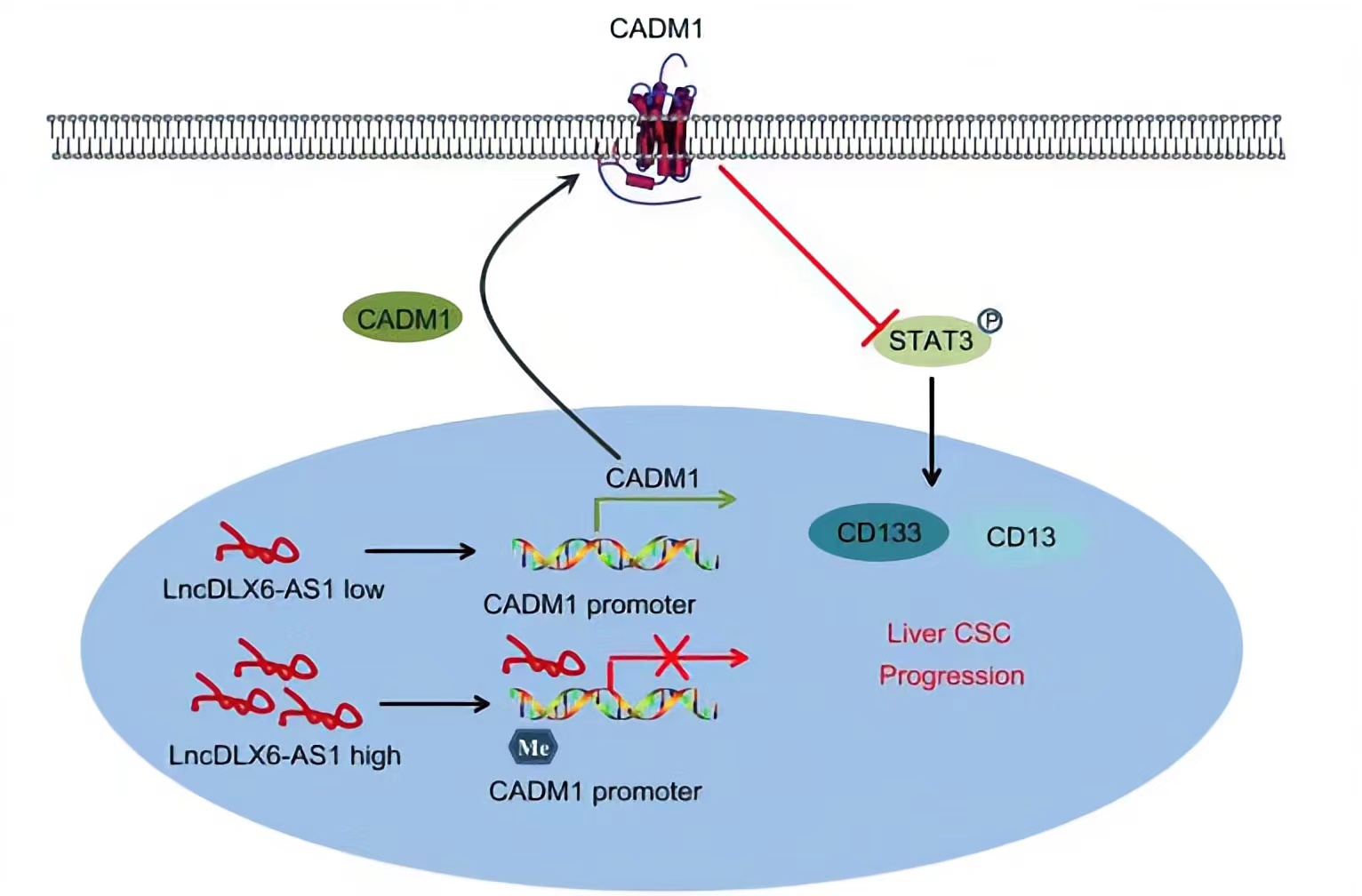
Conclusion
The LINC01419-EZH2 complex transcriptionally decreases RECK expression by binding at its H3K27me3 promoter.This contributes to HCC cell proliferation and metastasis.Elevated LINC01419 expression level results in poor outcomes in HCC. LINC01419 potentially suppresses RECK expression epigenetically via EZH2. LINC01419 upregulation is induced by the transcription activation of cjun. These findings proved that LINC01419 could provide a theoretical basis for clinical diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Regulatory Mechanism
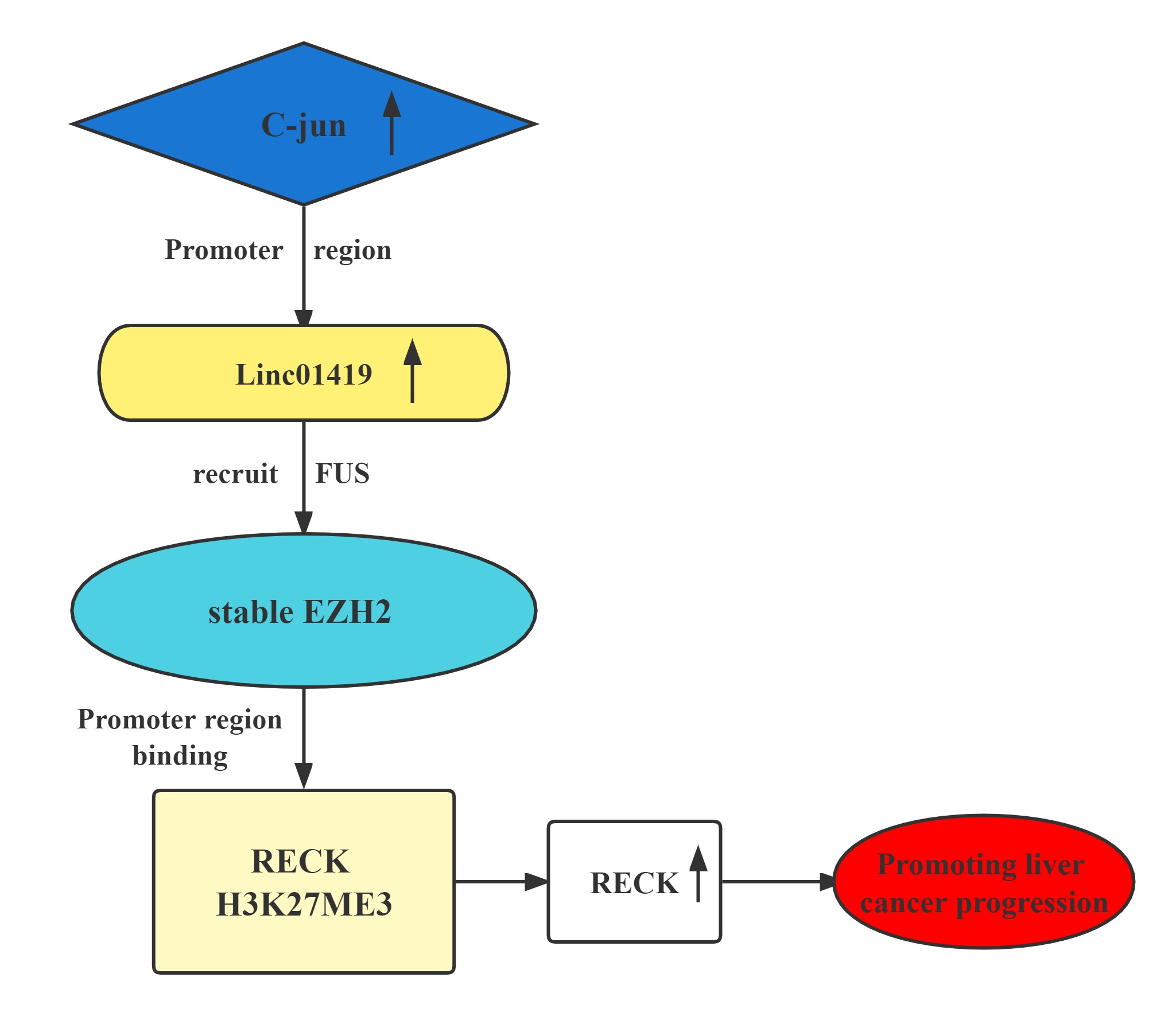
Conclusion
Lnc-Myd88 was located upstream of the protein-coding gene Myd88, and presented a reverse transcription direction with Myd88. On account of the results of ChIP assays conducted above, Lnc-Myd88 showed a positive correlation with the enrichment of H3K27Ac in the promoter region of Myd88, indicating that Lnc-Myd88 might regulate Myd88 expression through histone modifications.Lnc-Myd88 enhanced Myd88 expression through increasing the enrichment of H3K27Ac in the promoter region and then activated the NF-κB and PI3K/AKT signal pathways and then promoting the proliferation and metastasis of HCC both in vitro and in vivo.
Regulatory Mechanism
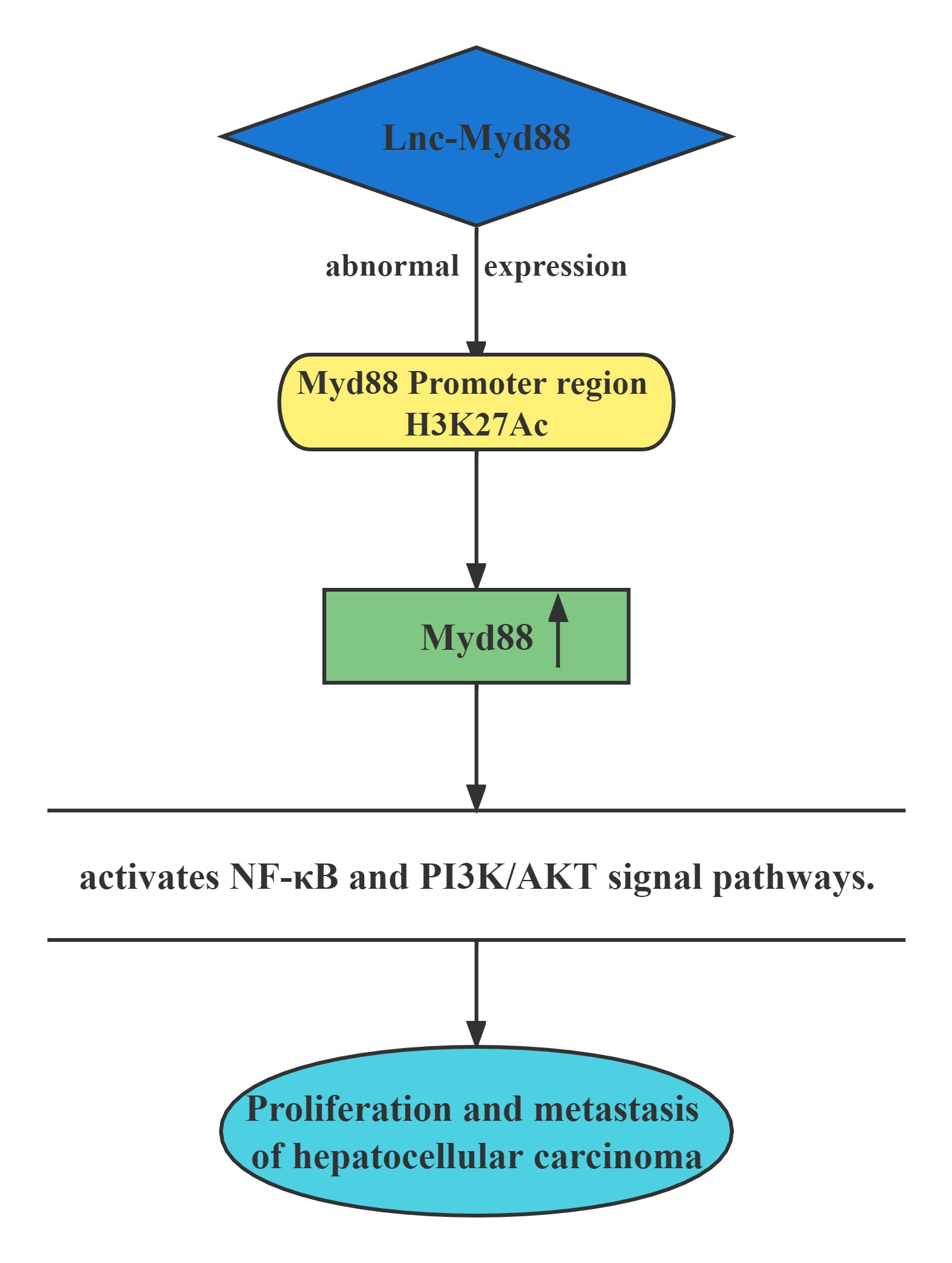
Conclusion
GPC3-AS1 and GPC3 expression in an independent cohort of HCC tissues.GPC3-AS1 and GPC3 are both upregulated in HCC tissues.GPC3-AS1 upregulation is associated with AFP, tumor size, microvascular invasion, encapsulation, and BCLC stage.GPC3-AS1 upregulates the transcription of GPC3, but does not change GPC3 mRNA stability.RNA pull-down, RIP, and ChIP assays showed that GPC3-AS1 physically associates with PCAF and recruits PCAF to the GPC3 gene body region. PCAF is a well-known histone acetyltransferase, which has important roles in transcription elongation.GPC3-AS1 binds to and recruits PCAF to the GPC3 gene body region, and upregulates GPC3 transcription. Through upregulating GPC3 expression, GPC3-AS1 enhances HCC cell proliferation and migration. These findings indicate that GPC3-AS1 could be a potential therapeutic target for HCC.
Regulatory Mechanism
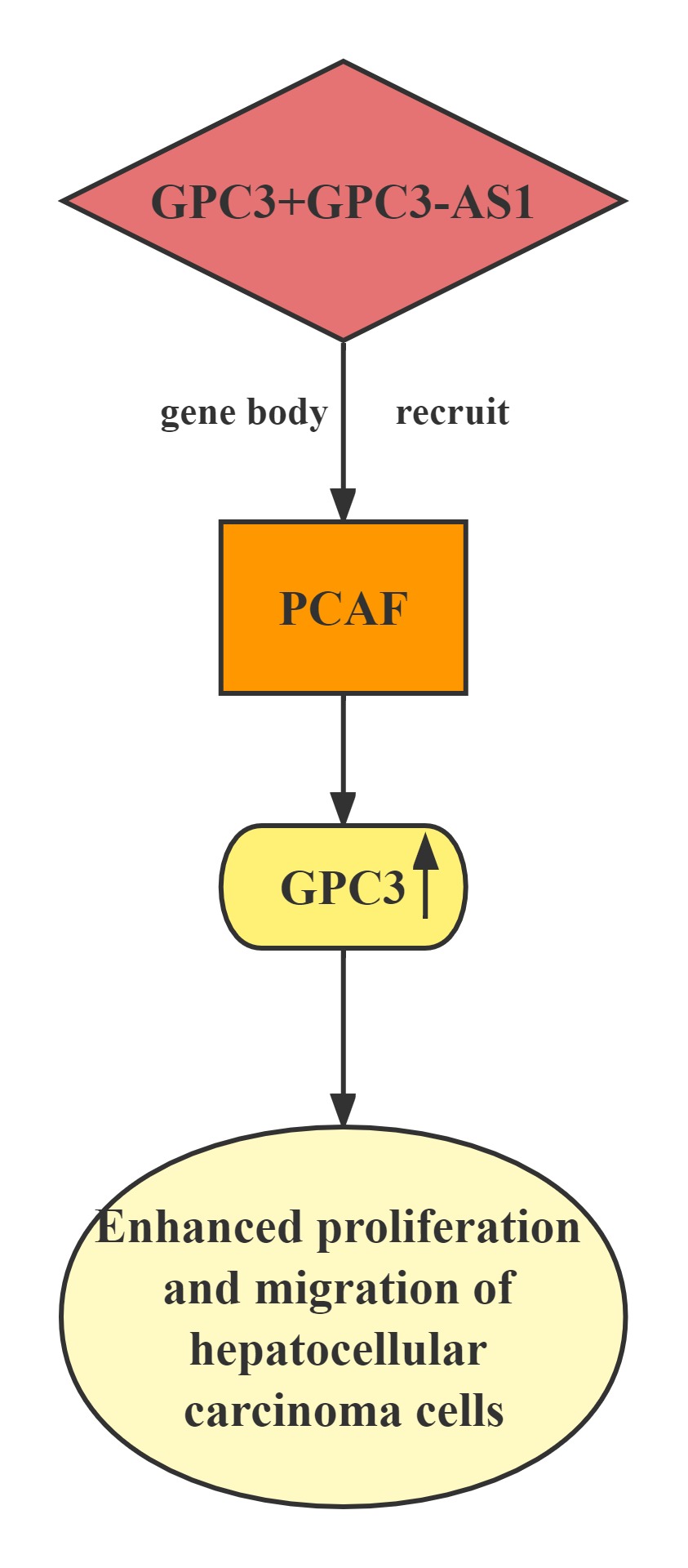
Lncrnas that act synergistically with histone transcription factor on target genes:
| ANRIL | TUG1 |
|---|
Conclusion
LncRNA ANRIL whose expression is significantly upregulated in HCC tissues compared with normal tissues.Increased ANRIL expression was correlated with HCC tumor size and BCLC stage, which suggests that ANRIL may play a key role in HCC development and progression.ANRIL could bind with both EZH2 and SUZ12 in HCC cells. Furthermore, bioinformatics analysis indicated that KLF2 could be a new ANRIL downstream target, and knockdown of ANRIL, EZH2 and SUZ12 expression indeed both up-regulated KLF2 expression levels in HCC cells. In addition, ChIP assays also demonstrated that EZH2 could directly bind to KLF2 promoter region and inhibition of ANRIL decreased its binding ability. ANRIL could repress KLF2 transcription by binding with EZH2 and SUZ12 and recruitment of PRC2 to the KLF2 gene locus in HCC cells.The Kruppel-like factor (KLF) family which consists of a set of transcription factors that have been identified in diverse organisms functions in cell differentiation and proliferation.
Regulatory Mechanism
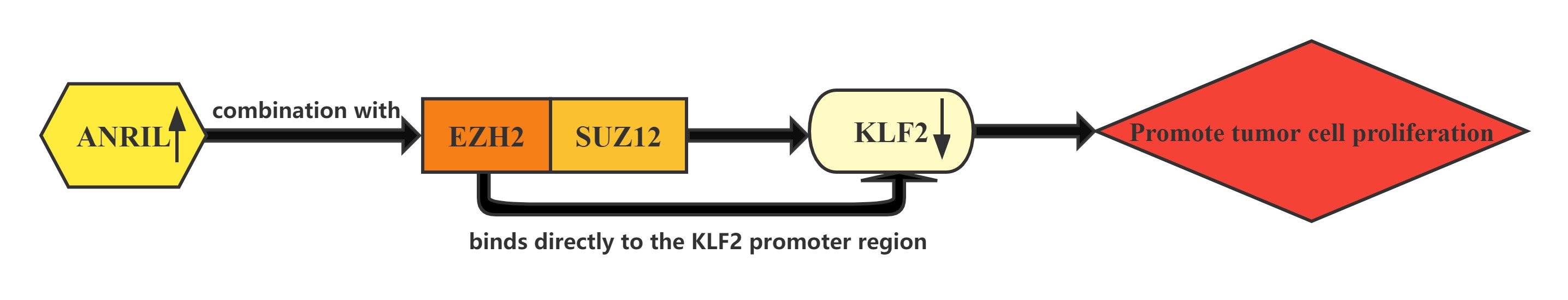
Conclusion
LncRNA TUG1 whose expression is significantly upregulated in HCC tissues compared with normal tissues.Increased TUG1 expression was correlated with HCC tumor size and BCLC stage, which suggests that TUG1 may play a key role in HCC development and progression.TUG1 could bind with both EZH2 and SUZ12 in HCC cells. Furthermore, bioinformatics analysis indicated that KLF2 could be a new TUG1 downstream target, and knockdown of TUG1, EZH2 and SUZ12 expression indeed both up-regulated KLF2 expression levels in HCC cells. In addition, ChIP assays also demonstrated that EZH2 could directly bind to KLF2 promoter region and inhibition of TUG1 decreased its binding ability. TUG1 could repress KLF2 transcription by binding with EZH2 and SUZ12 and recruitment of PRC2 to the KLF2 gene locus in HCC cells.The Kruppel-like factor (KLF) family which consists of a set of transcription factors that have been identified in diverse organisms functions in cell differentiation and proliferation.
Regulatory Mechanism

Lncrnas acting on target genes alone:
| SOX21-AS1 |
|---|
Conclusion
Silenced SOX21-AS1 suppressed cell proliferation and metastasis, resulted in cell cycle arrest, and induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mechanically, RIP was conducted to prove that SOX21-AS1 could bind with EZH2. ChIp assay was carried out and manifested that SOX21-AS1 epigenetically silenced p21 via recruiting EZH2 to the promoter of p21 to affect hepatocellular carcinoma progression.
Regulatory Mechanism
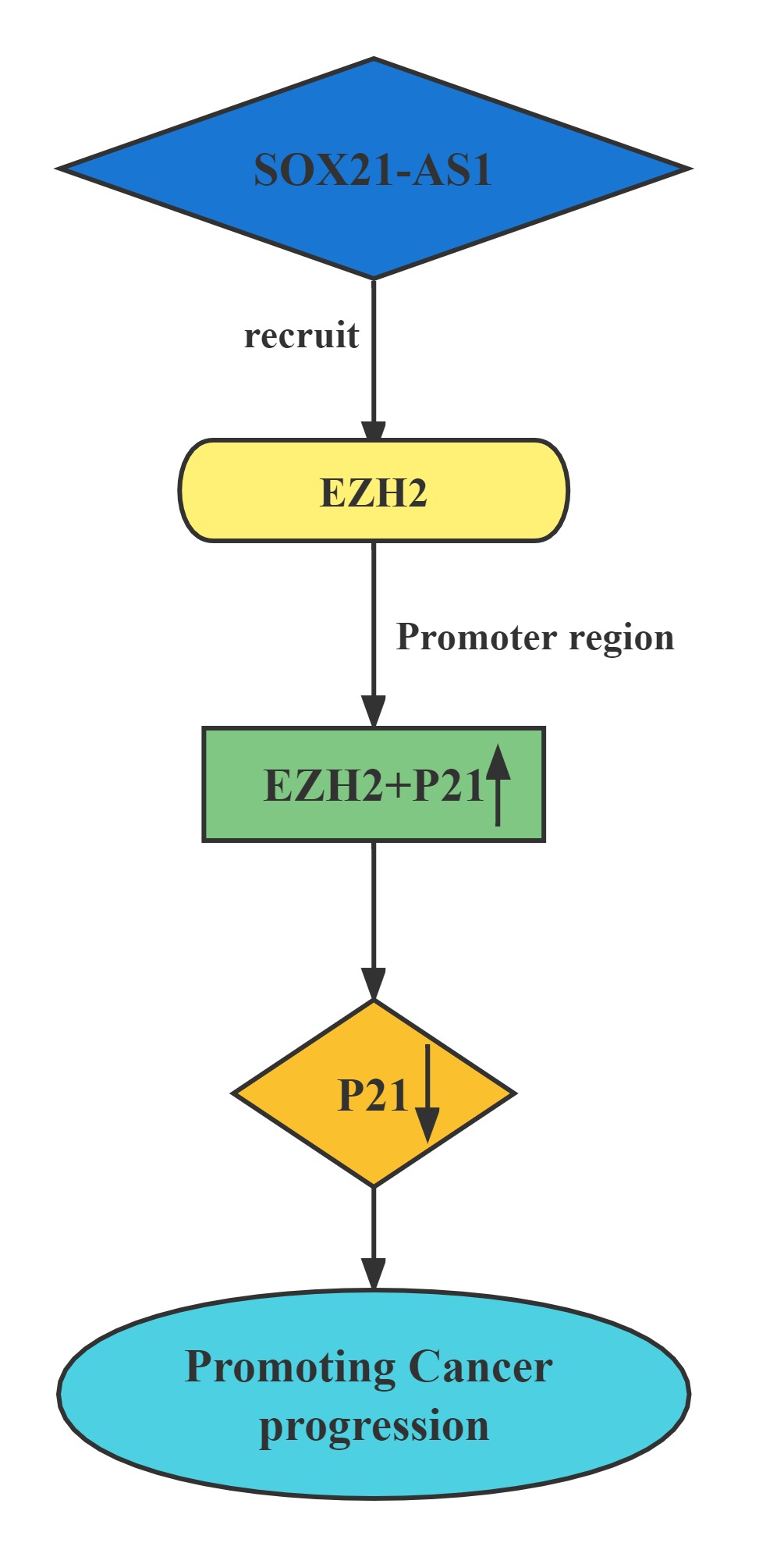
Lncrnas that act synergistically with RNA methylation on target genes:
| H19 |
|---|
Conclusion
A regulatory axis:MYC-NSUN2-H19G3BP1-MYC. In tumors, high expression of NSUN2 leads to increased methylation levels of H19 RNA. Hypermethylated H19 RNA may competitively bind to G3BP1, which further delays MYC mRNA decay and leads to a further increase in MYC levels, resulting in consequent deterioration of tumors.H19 RNA is a specific target for the NSUN2 modifier. The m5C-modified H19 lncRNA may promote the occurrence and development of tumors by recruiting the G3BP1 oncoprotein.
Regulatory Mechanism
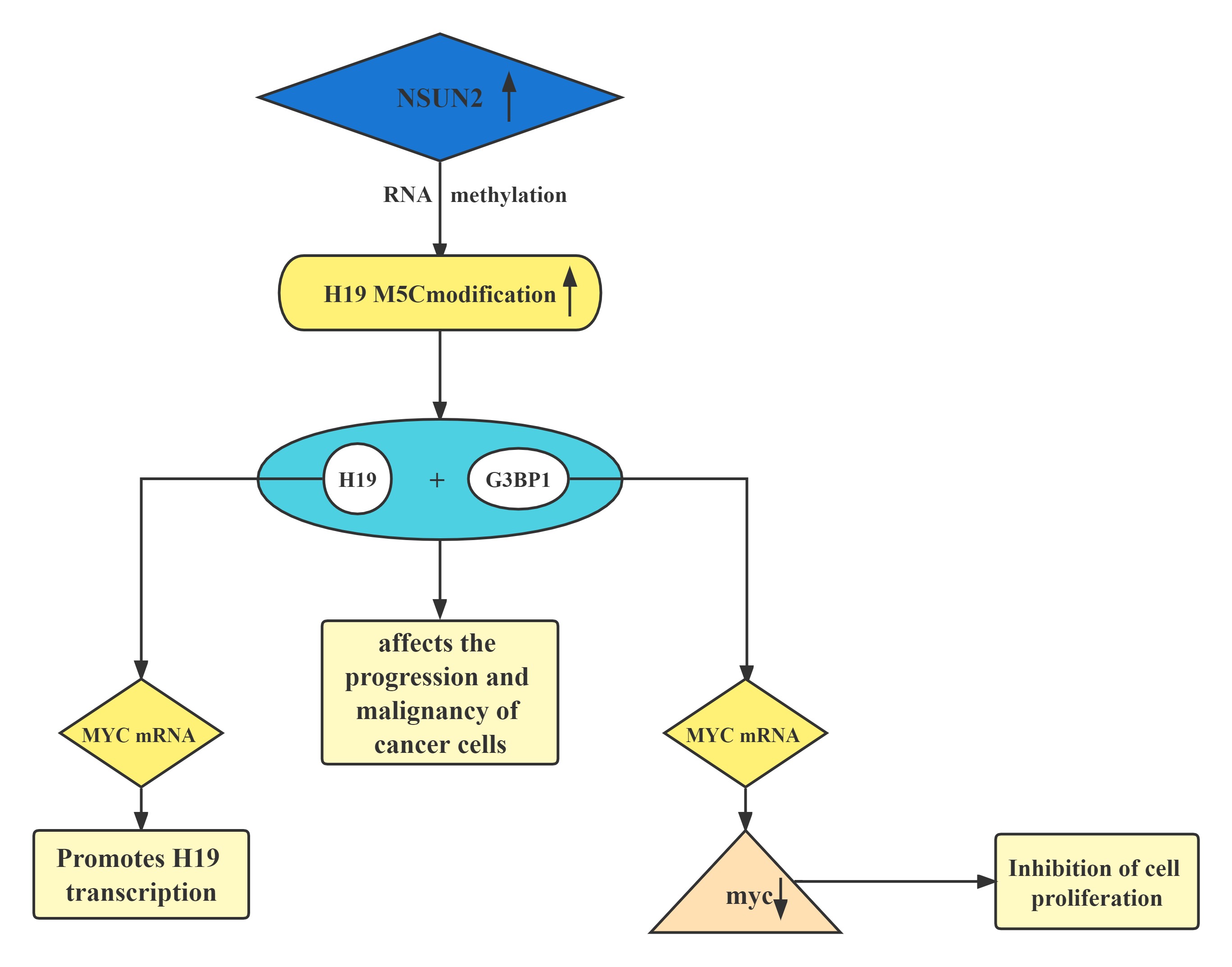
Lncrnas that act synergistically with methylation, histone modifications, and transcription factors on target genes:
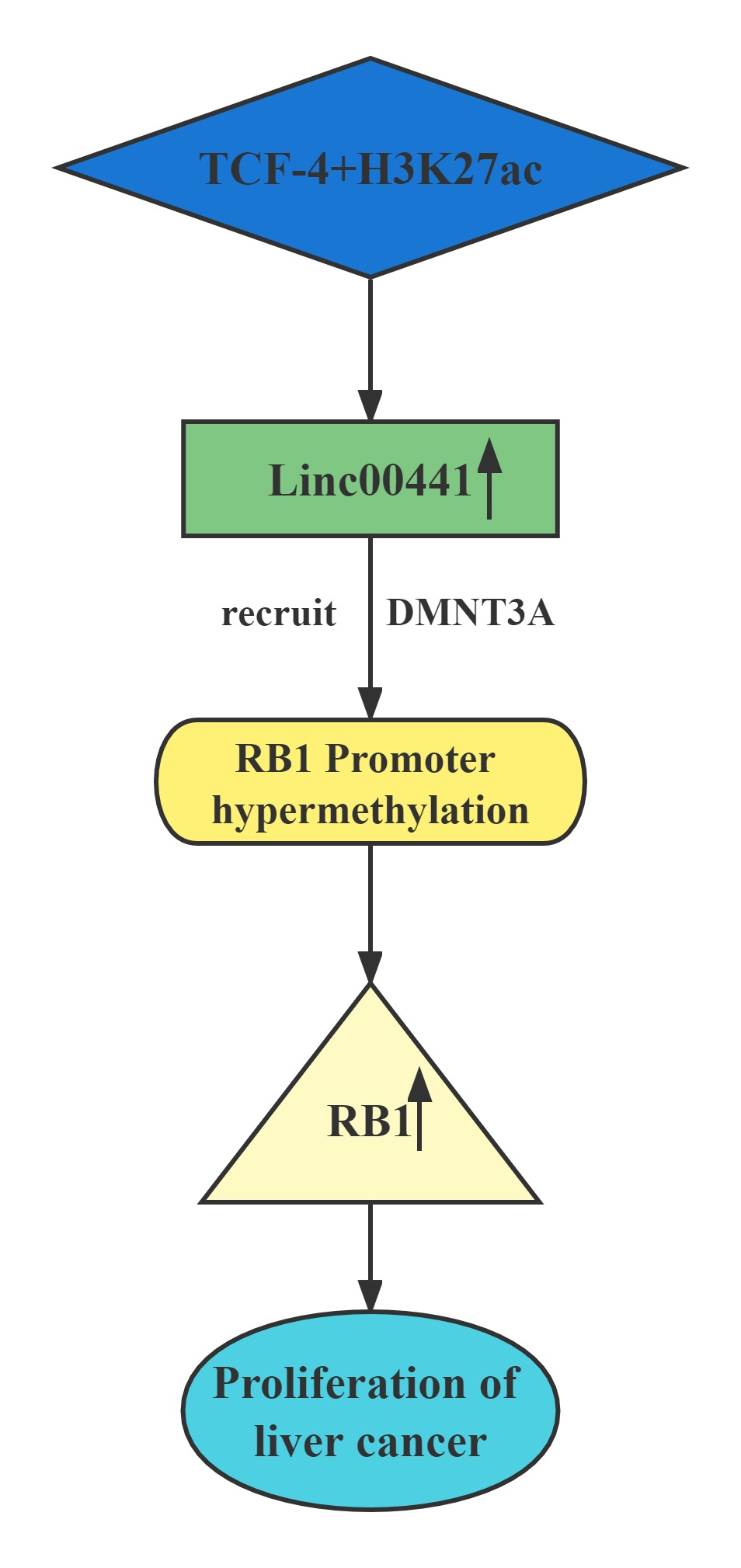
| Linc00441 |
|---|
Conclusion
Linc00441 share a bidirectional promoter with RB1.Aberrant upregulated intranuclear Linc00441 was inversely correlated with RB1 expression in human HCC samples. In vitro experiments, overexpression of Linc00441 could decrease the expression level of TSG RB1.Linc00441 may decrease RB1 expression through enhanced CpG islands methylation in the promoter of RB1 gene by DNMT3A recruitment, and afterward, causing proliferation of HCC in both in vitro and in vivo. TCF-4 and H3K27 acetylation also contributed to Linc00441 upregulation.
Regulatory Mechanism